Understanding Pigmentation

Understanding Pigmentation: Causes, Types, and Treatment Options
Pigmentation is a common skin concern that many people face at some point in their lives. It refers to the coloring of the skin, primarily determined by melanin, the pigment produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. While pigmentation can enhance your natural beauty, uneven skin tone or dark spots can be frustrating and may affect your confidence. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of pigmentation, their causes, and effective treatment options.
What Causes Pigmentation?
Pigmentation can result from various factors, including:
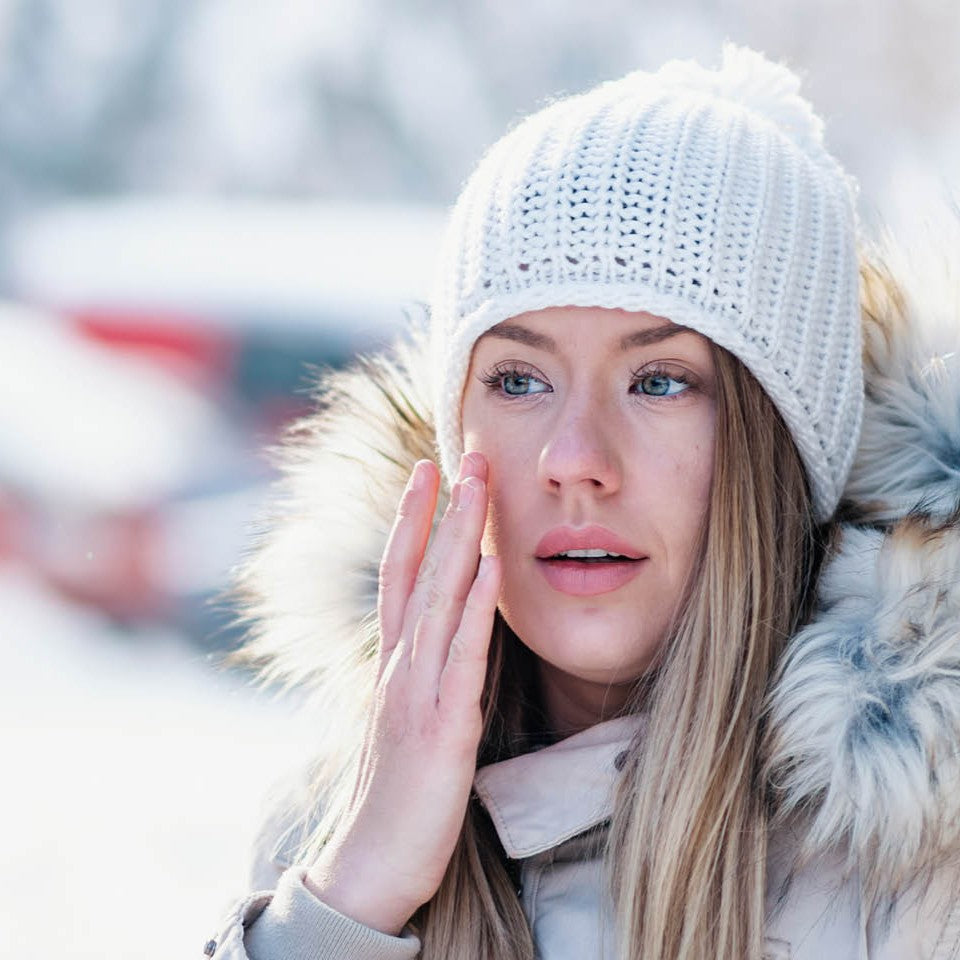
- Sun Exposure: One of the leading causes of pigmentation is UV radiation from the sun. Overexposure can lead to sun spots, also known as solar lentigines.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like melasma, often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy or contraceptive use, lead to dark patches on the face.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: After an injury, acne, or any inflammatory condition, the skin may produce excess melanin, resulting in dark spots.
- Genetics: Your genetic makeup can play a role in how your skin reacts to sun exposure and other environmental factors.
- Ageing: As we age, the skin may become more prone to pigmentation issues due to the cumulative effects of sun damage over the years.
Types of Pigmentation
- Sun Spots (Lentigines): Flat, brown spots that appear on sun-exposed areas, commonly found on the face, hands, and arms.
- Melasma: Characterized by larger brown patches on the face, melasma is often associated with hormonal changes and is more common in women.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots that occur after skin injuries or conditions like acne, eczema, or psoriasis.
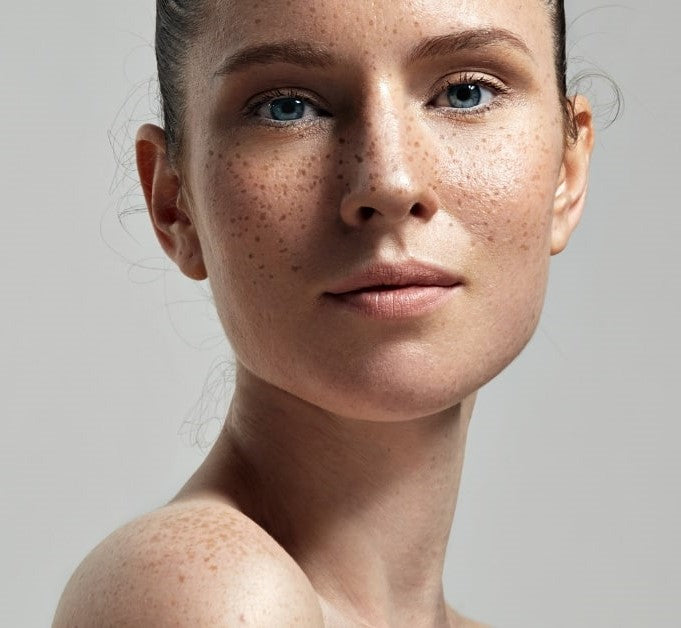
- Freckles: Small, light brown spots that can be genetic and usually become more pronounced with sun exposure.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available for pigmentation issues:
- Topical Treatments:
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives promote skin cell turnover, helping to fade pigmentation over time.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that can brighten the skin and inhibit melanin production, reducing the appearance of dark spots.
- Chemical Peels: These treatments use acids to exfoliate the top layer of skin, promoting new cell growth and reducing pigmentation.
- Microneedling: This procedure creates tiny wounds in the skin, stimulating collagen production and helping to improve skin texture and tone.
- Sun Protection: Prevention is crucial. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily can help protect your skin from UV damage, preventing further pigmentation.
Tips for Managing Pigmentation
- Be Consistent: Follow a dedicated skincare routine with the recommended products for at least a few weeks to see noticeable results.
- Hydrate: Keeping your skin moisturized can enhance its overall appearance and help it recover from pigmentation.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re unsure about the best treatment for your skin, consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Conclusion
Pigmentation issues are common but manageable with the right approach. By understanding the causes and exploring various treatment options, you can achieve a more even skin tone and boost your confidence. Remember, prevention is key—always protect your skin from the sun and maintain a consistent skincare regimen. If you’re dealing with persistent pigmentation concerns, consider consulting a dermatologist for tailored advice and treatment plans.